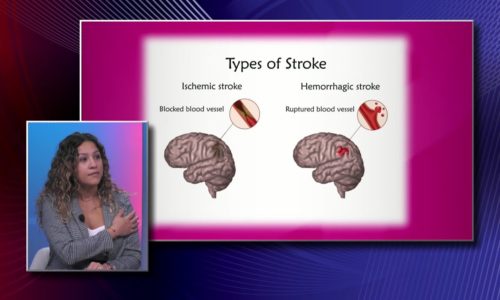
Ischemic and Hemorrhagic Strokes: Understanding the Differences |
 Strokes are a medical emergency that require prompt attention. They occur when the blood supply to the brain is interrupted, leading to brain cell damage or death. In general, there are two types of strokes: ischemic and hemorrhagic. In this article, we will discuss these two types of strokes and their differences.
Strokes are a medical emergency that require prompt attention. They occur when the blood supply to the brain is interrupted, leading to brain cell damage or death. In general, there are two types of strokes: ischemic and hemorrhagic. In this article, we will discuss these two types of strokes and their differences.
- Ischemic Stroke
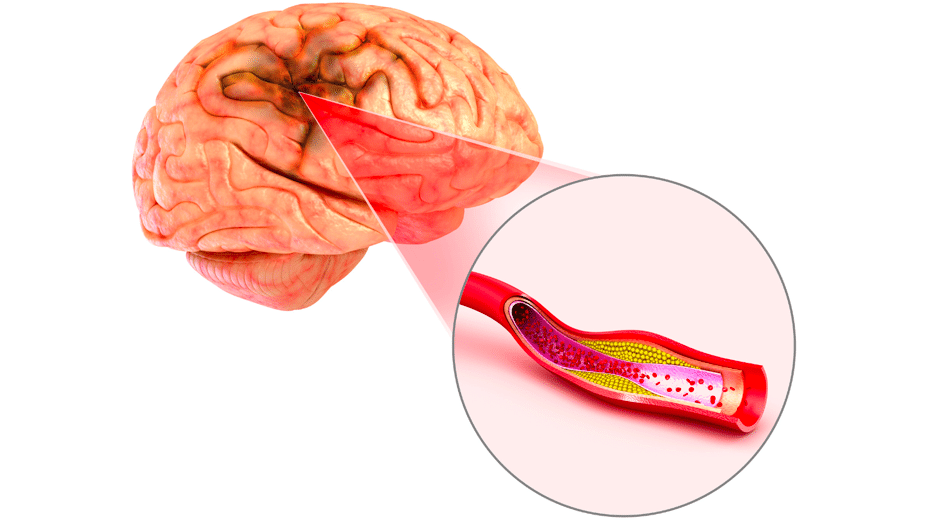
The most common type of stroke is an ischemic stroke. This type of stroke occurs when the blood flow to the brain is blocked or reduced. This blockage can be caused by a blood clot or a buildup of plaque in the blood vessels that supply blood to the brain.
The symptoms of an ischemic stroke can vary depending on the location of the blockage in the brain. However, common symptoms include changes in vision, speech, or weakness on one side of the body. The severity of the symptoms can also vary, ranging from mild to severe.
- Hemorrhagic Stroke
A hemorrhagic stroke, on the other hand, occurs when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures, causing bleeding in or around the brain. The bleeding can increase pressure on the brain and cause damage to brain cells.
Hemorrhagic strokes can be caused by high blood pressure or the rupture of an aneurysm. Aneurysms are bulges in the walls of blood vessels that can weaken and rupture over time.
The symptoms of a hemorrhagic stroke can also vary depending on the location and severity of the bleeding. Common symptoms include sudden severe headache, nausea, vomiting, seizures, and loss of consciousness.
- Ischemic vs Hemorrhagic Strokes
Ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes have some similarities in symptoms, but their causes and treatment methods differ. Ischemic strokes are more common than hemorrhagic strokes, accounting for about 87% of all strokes. Hemorrhagic strokes, on the other hand, are less common but can be more dangerous.
Ischemic strokes are typically treated with medications that can dissolve blood clots or surgery to remove the clot. Hemorrhagic strokes, however, are treated differently, as clot-busting medications can increase bleeding in the brain. Treatment for hemorrhagic strokes may include controlling blood pressure, surgery to repair the damaged blood vessel, or medication to reduce swelling in the brain.
Preventing strokes is essential to maintaining good health. Some risk factors for strokes include high blood pressure, smoking, obesity, and high cholesterol levels. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding smoking can all help to reduce your risk of stroke.
In conclusion, strokes are a serious medical emergency that requires prompt attention. Ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes differ in their causes and treatment methods, and recognizing the symptoms of each type of stroke is important for proper diagnosis and treatment. Taking steps to reduce your risk of stroke can help you maintain good health and prevent serious complications.