Diagnosing of Spinal Fractures |
When a patient presents with symptoms that suggest a compression fracture, it is essential to conduct a thorough physical examination to aid in diagnosis and treatment planning. This article explores some of the critical elements that healthcare professionals assess during a physical exam to identify potential compression fractures. By understanding these indicators, healthcare providers can better evaluate the patient’s condition and develop an appropriate management strategy.
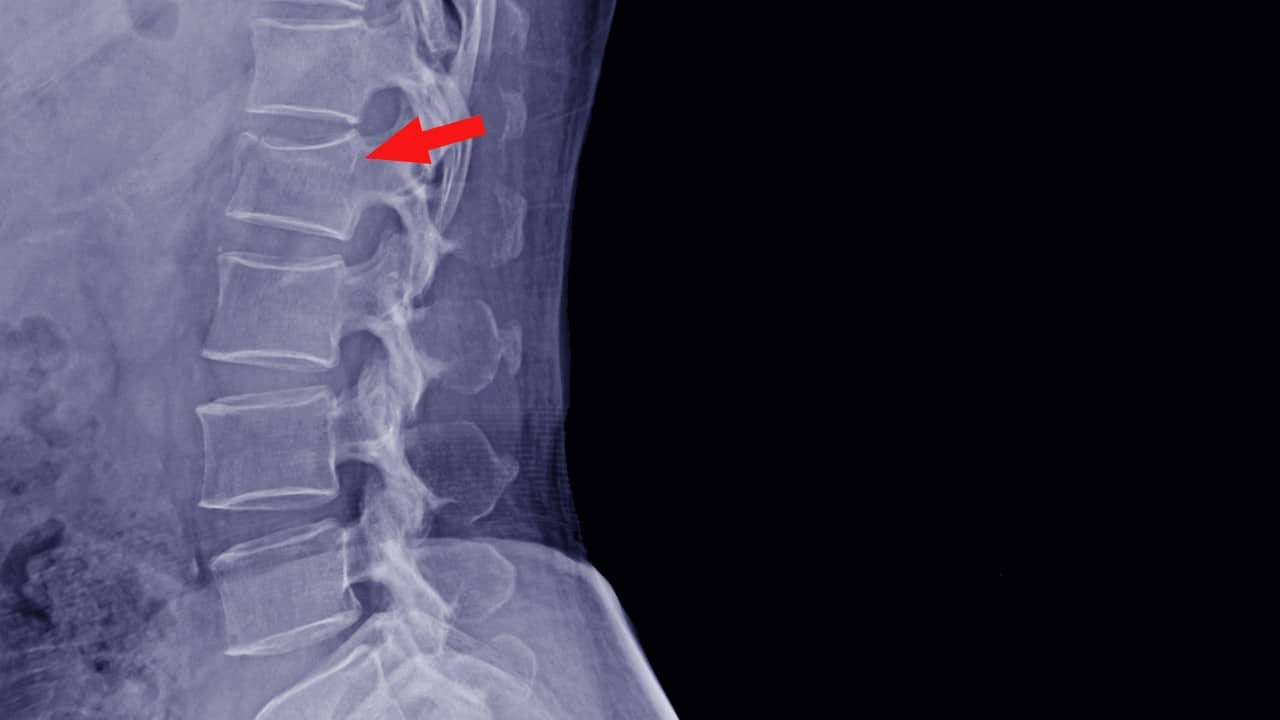
One of the key aspects of the physical examination is to evaluate the patient’s spinal alignment. Healthcare providers look for signs of a humpback or kyphosis, which refers to an abnormal forward curvature of the upper back. This visual assessment helps determine if there are any visible abnormalities in the spine’s structure that may indicate a compression fracture.
Another crucial aspect of the physical examination is to check for tenderness over the affected spinal bone or bones. Healthcare providers gently palpate the spine, focusing on pinpoint tenderness in the center of the spine, specifically at the level where the patient reports pain. This tenderness serves as a localized indicator of potential compression fractures.
A comprehensive physical examination for compression fractures includes a neurological assessment. Healthcare providers evaluate for any neurological deficits that may indicate nerve compression. They check for weakness, foot drop (inability to lift the front part of the foot), and assess the patient’s sensation. The absence of significant neurological deficits suggests minimal compression of the nerves in the spine.
In addition to assessing pain and neurological symptoms, healthcare providers conduct a gait examination to evaluate the patient’s walking ability and overall functionality. They observe how the patient stands, sits, and moves. Time-stand-to-sit, which measures the time it takes for the patient to get up and walk a short distance, provides valuable insights into their mobility. Patients with compression fractures may exhibit difficulty standing up, relying on their arms for support and exhibiting signs of discomfort.
Evaluating the patient’s overall spinal alignment and posture offers valuable information about the presence of past fractures. An assessment of kyphosis or stooped posture can indicate not only the current compression fracture but also the potential for multiple fractures in the past. Understanding the patient’s history of fractures helps healthcare providers better comprehend the chronicity and severity of the condition.
A thorough physical examination is crucial in identifying and evaluating compression fractures. Healthcare providers assess for visible abnormalities in spinal alignment, tenderness over affected spinal bones, and potential neurological deficits. Gait examination provides insights into mobility and functionality, while spinal alignment and posture indicate the presence of past fractures. By conducting a comprehensive physical examination, healthcare professionals can gather essential information to guide diagnosis, treatment planning, and ongoing management of compression fractures.
To find out more about compression fractures and their causes, you can check out more videos on fractures on the Health Channel YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0DQuDfl0pc4